In recent years, robotics has significantly revolutionized the manufacturing and automation industries, shaping how products are designed, produced, and delivered. The impact of robotics extends beyond traditional automation to include advanced artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and the Internet of Things (IoT). These technologies are creating smart factories where robots and machines operate seamlessly, offering unprecedented levels of precision, efficiency, and scalability. In this article, we’ll explore how robotics is transforming manufacturing and automation, the benefits and challenges of this transformation, and what the future holds for industries embracing robotic technologies.
The Evolution of Robotics in Manufacturing
Early Days of Industrial Robots
Robotics has been part of manufacturing since the 1960s, with the introduction of early industrial robots like Unimate, which was used to automate the assembly line at General Motors. These early robots were designed to perform repetitive tasks such as welding, painting, and material handling with more accuracy than human workers, reducing production time and costs.
The Integration of Advanced Robotics
As technology evolved, so did the role of robotics in manufacturing. The integration of more advanced robotics—equipped with sensors, machine learning, and AI—pushed the industry into the era of smart manufacturing. These robots are capable of performing complex tasks, learning from their environment, and adapting to new conditions.
The Rise of Collaborative Robots (Cobots)
A significant milestone in robotics has been the rise of collaborative robots, or “cobots.” Cobots are designed to work alongside human workers, assisting them with tasks that require both precision and flexibility. Unlike traditional robots, which were often confined to isolated areas of the factory, cobots enhance human productivity and reduce risks by taking over tasks that are dangerous or repetitive.
How Robotics Is Transforming Manufacturing
Increased Efficiency and Productivity
One of the most significant advantages of robotics in manufacturing is the increase in efficiency and productivity. Robots can work continuously without fatigue, resulting in higher output and shorter production cycles. They also eliminate errors that can occur with human labor, ensuring greater consistency in quality.
Enhanced Precision and Quality Control
Robots excel at performing tasks that require a high degree of precision. In industries such as electronics, aerospace, and automotive manufacturing, even the smallest deviation can lead to product failure. Robotics systems equipped with AI can detect potential quality issues in real time, allowing manufacturers to address defects before they escalate.
Reduction of Labor Costs
With robots taking over routine and repetitive tasks, businesses can reduce labor costs and reallocate human workers to more strategic and creative roles. This shift is particularly valuable in regions where labor shortages are becoming a challenge. Additionally, robots can perform tasks that are dangerous to human health, reducing workplace injuries and related costs.
Flexibility in Production Lines
Modern robotics are highly flexible and adaptable, allowing manufacturers to switch between products with minimal downtime. For example, robots can be reprogrammed to handle new tasks as production needs change, making them essential in industries that require customization or rapid changes in output.
Robotics and Automation Technologies
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Robotics
The integration of AI and ML with robotics has further enhanced the capabilities of automation systems. AI-powered robots can process vast amounts of data, identify patterns, and make decisions based on this information. In a factory setting, this allows for predictive maintenance, improved logistics, and enhanced quality control.
Robotics and IoT: The Connected Factory
The Internet of Things (IoT) has also played a crucial role in transforming manufacturing automation. IoT sensors can connect machines and robots across the factory floor, enabling real-time monitoring and control. This interconnected system allows for seamless communication between different devices, optimizing processes and reducing energy consumption.
Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) for Material Handling
Autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) are revolutionizing the logistics and material handling processes in manufacturing. These robots can navigate factory floors independently, delivering materials and parts where they are needed without human intervention. AMRs rely on advanced sensors and navigation systems to avoid obstacles and respond to changing environments, increasing overall factory efficiency.
3D Printing and Robotics
Robotics and 3D printing (additive manufacturing) are complementary technologies that are reshaping manufacturing processes. 3D printing allows for the creation of complex, customized components, and robots can assist in handling and assembling these parts. Together, they enable faster prototyping, lower production costs, and more efficient use of materials.
Applications of Robotics in Various Manufacturing Sectors
Automotive Manufacturing
The automotive industry has long been a leader in adopting robotics for tasks such as welding, painting, and assembling parts. Today, robots are also being used for more advanced functions like inspecting parts, ensuring precise measurements, and enhancing the safety of workers by performing hazardous tasks.
Electronics and Semiconductor Manufacturing
Robotics plays a crucial role in the electronics industry, where precision is critical. Robots are used to assemble intricate components such as circuit boards, where human error could lead to costly malfunctions. The use of robotics in semiconductor manufacturing also helps to maintain the sterile environments necessary for producing microchips.
Food and Beverage Industry
Robots are transforming food production by automating processes such as packaging, labeling, and palletizing. They ensure consistent quality and hygiene, which is essential in the food and beverage sector. In addition, robots can handle delicate items, like fruits and vegetables, reducing product waste.
Pharmaceuticals and Biotechnology
In the pharmaceutical industry, robots are employed in tasks such as drug manufacturing, packaging, and even conducting lab research. Their use ensures accuracy, sterility, and safety, especially in environments where contamination must be avoided. Additionally, robots are aiding in the development and testing of new drugs, reducing the time to market.
Benefits of Robotics in Automation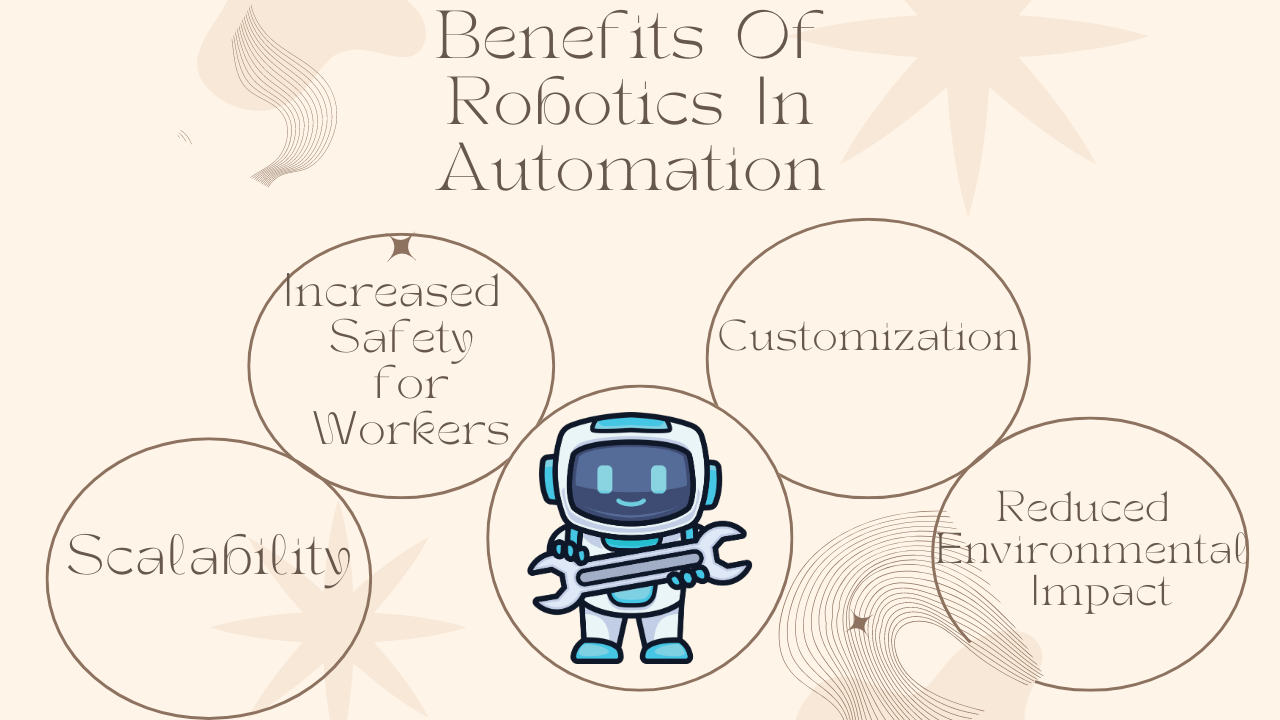
Increased Safety for Workers
One of the primary benefits of robotics in manufacturing is enhanced worker safety. Robots can take over dangerous tasks, such as working in extreme temperatures or handling toxic materials, reducing the risk of workplace injuries and accidents.
Scalability and Customization
Robots provide manufacturers with the ability to scale operations quickly and adapt to changing consumer demands. Whether a company needs to increase production or introduce a new product, robots offer the flexibility to adjust without the need for significant factory overhauls.
Reduced Environmental Impact
Many modern robots are energy-efficient and contribute to sustainable manufacturing practices. They can reduce waste by optimizing processes and materials usage, and their precision reduces the need for rework, further minimizing resource consumption.
Challenges in Adopting Robotics
High Initial Costs
While robotics can offer long-term cost savings, the initial investment in robots and automation systems can be significant. Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) may find it difficult to justify the upfront costs of integrating robotics into their production lines.
Workforce Displacement and Training Needs
One of the most debated challenges of robotics in manufacturing is the potential displacement of human workers. As robots take over repetitive tasks, there is a growing need to reskill and upskill the workforce to handle more strategic and technical roles. Companies must invest in training programs to ensure that workers are equipped to thrive in an automated environment.
Integration and Maintenance
Integrating robotics into existing manufacturing systems can be complex, requiring new infrastructure and software systems. Additionally, maintaining and updating these robots requires technical expertise, which may be a challenge for some organizations.
The Future of Robotics in Manufacturing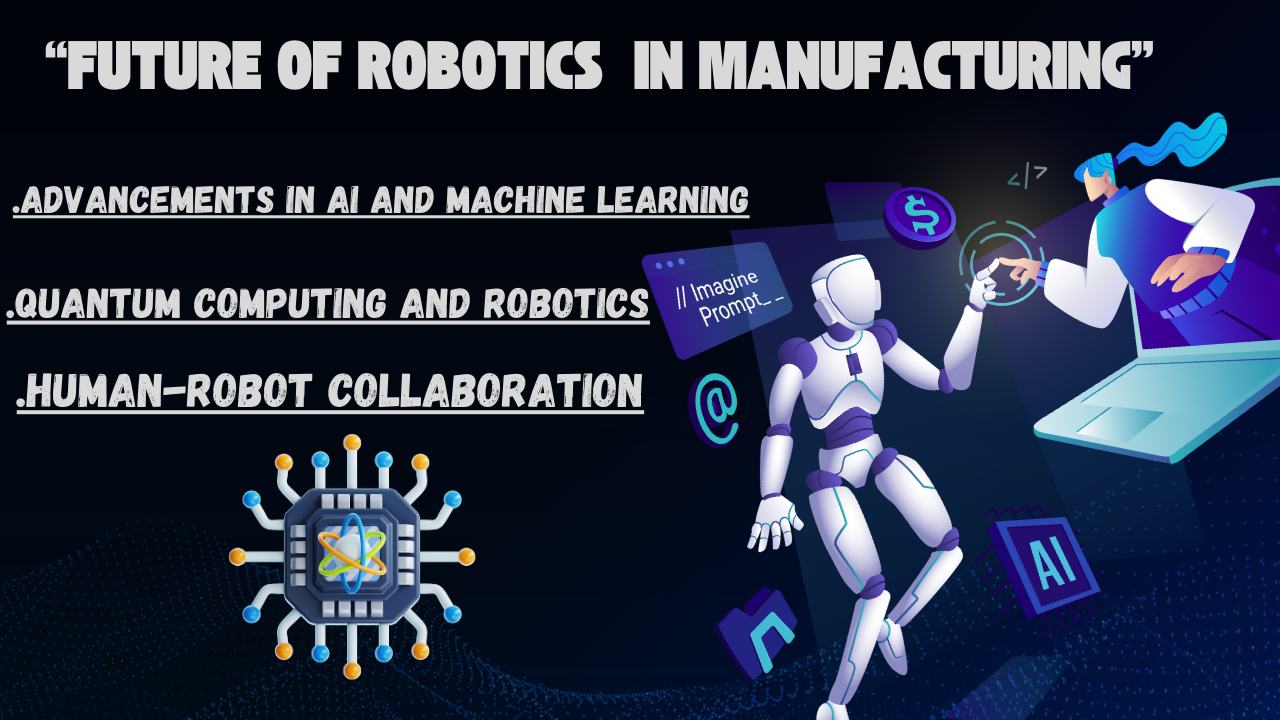
Advancements in AI and Machine Learning
As AI and ML continue to evolve, we can expect robots to become even more autonomous and intelligent. This will enable greater decision-making capabilities, allowing robots to perform more complex tasks without human intervention.
Quantum Computing and Robotics
Quantum computing is poised to revolutionize robotics by providing unprecedented computational power. This could lead to more sophisticated robotic algorithms, improving everything from real-time data processing to advanced simulations for optimizing manufacturing processes.
Human-Robot Collaboration
The future of manufacturing is likely to involve more human-robot collaboration. Rather than replacing humans, robots will assist workers in performing their tasks more efficiently. Innovations in human-robot interaction (HRI) will make these collaborations more intuitive and seamless.
Conclusion
Robotics is transforming manufacturing and automation in ways that were unimaginable a few decades ago. From increasing productivity and precision to enhancing safety and flexibility, robots are reshaping industries across the globe. As AI, ML, and IoT continue to evolve, the potential for robotics in manufacturing will only grow, enabling smarter, more efficient, and sustainable factories. While challenges such as high costs and workforce displacement exist, the benefits of robotics far outweigh the drawbacks, positioning it as a cornerstone of the future of manufacturing.
FAQs
What are the main benefits of using robotics in manufacturing?
Robotics enhances productivity, precision, and safety while reducing labor costs and allowing for greater flexibility in production.
What is the difference between industrial robots and collaborative robots (cobots)?
Industrial robots typically work in isolated areas performing repetitive tasks, while cobots work alongside humans, assisting with tasks that require precision and flexibility.
How is AI integrated with robotics in manufacturing?
AI enables robots to learn from data, make decisions, and improve their performance over time, leading to smarter automation systems.
What industries are most impacted by robotics?
Automotive, electronics, pharmaceuticals, food and beverage, and aerospace are among the industries most impacted by robotics.
What are the challenges of adopting robotics in manufacturing?
High initial costs, the need for skilled workers, and the complexity of integrating robotics into existing systems are some of the